With the AI revolution spreading across industries everywhere, NVIDIA founder and CEO Jensen Huang took the stage Wednesday to unveil the latest technology for speeding its mass adoption.
His talk — to more than 6,000 scientists, engineers and entrepreneurs gathered for this week’s GPU Technology Conference in Suzhou, two hours west of Shanghai — touched on advancements in AI deployment, as well as NVIDIA’s work in the automotive, gaming, and healthcare industries.
“We build computers for the Einsteins, Leonardo di Vincis, Michaelngelos of our time,” Huang told the crowd, which overflowed into the aisles. “We build these computers for all of you.”

Huang explained that demand is surging for technology that can accelerate the delivery of AI services of all kinds. And NVIDIA’s deep learning platform — which the company updated Wednesday with new inferencing software — promises to be the fastest, most efficient way to deliver these services.
It’s the latest example of how NVIDIA achieves spectacular speedups by applying a combination of GPUs optimized for parallel computation, work across the entire computing stack, and algorithm and ecosystem expertise in focused vertical markets.
“It is accepted now that GPU accelerated computing is the path forward as Moore’s law has ended,” Huang said.
Real-Time Recommendations: Baidu and Alibaba
The latest challenge for accelerated computing: driving a new generation of powerful systems, known as recommender systems, able to connect individuals with what they’re looking for in a world where the options available to them is spiraling exponentially.
“The era of search has ended: if I put out a trillion, billion million things and they’re changing all the time, how can you find anything,” Huang asked. “The era of search is over. The era of recommendations has arrived.
Baidu — one of the world’s largest search companies – is harnessing NVIDIA technology to power advanced recommendation engines.
“It solves this problem of taking this enormous amount of data, and filtering it through this recommendation system so you only see 10 things,” Huang said.
With GPUs, Baidu can now train the models that power its recommender systems 10x faster, reducing costs, and, over the long term, increasing the accuracy of its models, improving the quality of its recommendations.
Another example such systems’ power: Alibaba, which relies on NVIDIA technology to help power the recommendation engines behind the success of Single’s Day.
This new shopping festival which takes place on Nov. 11 — or 11.11 — generated $38 billion in sales last month. That’s up by nearly a quarter from last year’s $31 billion, and more than double the online sales on Black Friday and Cyber Monday combined.
Helping to drive its success are recommender systems that display items that match user preferences, improving the click-through rate — which is closely watched in the e-commerce industry as a key sales driver. Its systems need to run in real-time and at an incredible scale, something that’s only possible with GPUs.
“Deep learning inference is wonderful for deep recommender systems and these recommender systems will be the engine for the Internet,” Huang said. “Everything we do in the future, everything we do now, passes through a recommender system.”
Real-Time Conversational AI
Huang also announced groundbreaking new inference software enabling smarter, real-time conversational AI.
NVIDIA TensorRT 7 — the seventh generation of the company’s inference software development kit — features a new deep learning compiler designed to automatically optimize and accelerate the increasingly complex recurrent and transformer-based neural networks needed for complex new applications, such as AI speech.

This speeds the components of conversational AI by 10x compared to CPUs, driving latency below the 300-millisecond threshold considered necessary for real-time interactions.
“To have the ability to understand your intention, make recommendations, do searches and queries for you, and summarize what they’ve learned to a text to speech system… that loop is now possible,” Huang said. “It is now possible to achieve very natural, very rich, conversational AI in real time.”
Accelerating Automotive Innovations
Huang also announced NVIDIA will provide the transportation industry with source access to its NVIDIA DRIVE deep neural networks (DNNs) for autonomous vehicle development.
NVIDIA DRIVE has become a de facto standard for AV development, used broadly by automakers, truck manufacturers, robotaxi companies, software companies and universities.
Now, NVIDIA is providing source access of it’s pre-trained AI models and training code to AV developers. Using a suite of NVIDIA AI tools, the ecosystem can freely extend and customize the models to increase the robustness and capabilities of their self-driving systems.
In addition to providing source access to the DNNs, Huang announcing the availability of a suite of advanced tools so developers can customize and enhance NVIDIA’s DNNs, utilizing their own data sets and target feature set. These tools allow the training of DNNs utilizing active learning, federated learning and transfer learning, Huang said.
Haung also announced NVIDIA DRIVE AGX Orin, the world’s highest performance and most advanced system-on-a-chip. It delivers 7x the performance and 3x the efficiency per watt of Xavier, NVIDIA’s previous-generation automotive SoC. Orin — which will be available to be incorporated in customer production runs for 2022 — boasts 17 billion transistors, 12 CPU cores, and is capable of over 200 trillion operations per second.
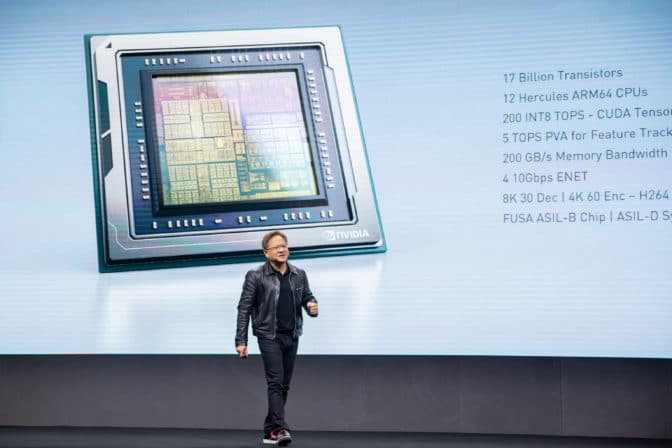

Orin will be woven into a stack of products — all running a single architecture and compatible with software developed on Xavier — able to scale from simple level 2 autonomy, all the way up to full Level 5 autonomy.
And Huang announced that Didi — the world’s largest ride hailing company — will adopt NVIDIA DRIVE to bring robotaxis and intelligent ride-hailing services to market.
“We believe everything that moves will be autonomous some day,” Huang said. “This is not the work of one company, this is the work of one industry, and we’ve created an open platform so we can all team up together to realize this autonomous future.”
Game On
Adding to NVIDIA’s growing footprint in cloud gaming, Huang announced a collaboration with Tencent Games in cloud gaming.
“We are going to extend the wonderful experience of PC gaming to all the computers that are underpowered today, the opportunity is quite extraordinary,” Huang said. “We can extend PC gaming to the other 800 milliion gamers in the world.”
NVIDIA’s technology will power Tencent Games’ START cloud gaming service, which began testing earlier this year. START gives gamers access to AAA games on underpowered devices anytime, anywhere.

Huang also announced that six leading game developers will join the ranks of game developers around the world who have been using the realtime ray tracing capabilities of NVIDIA’s GeForce RTX to transform the image quality and lighting effects of their upcoming titles
Ray tracing is a graphics rendering technique that brings real-time, cinematic-quality rendering to content creators and game developers. NVIDIA GeForce RTX GPUs contain specialized processor cores designed to accelerate ray tracing so the visual effects in games can be rendered in real time.
The upcoming games include a mix of blockbusters, new franchises, triple-A titles and indie fare — all using real-time ray tracing to bring ultra-realistic lighting models to their gameplay.
They include Boundary, from Surgical Scalpels Studios; Convallarioa, from LoongForce; F.I.S.T. from Shanghai TiGames; an unnamed project from Mihyo; Ring of Elysium, from TenCent; and Xuan Yuan Sword VII from Softstar.
Accelerating Medical Advances, 5G
This year, Huang said, NVIDIA has added two major new applications to CUDA – 5G vRAN and genomic processing. With each, NVIDIA’s supported by world leaders in their respective industries – Ericsson in telecommunication and BGI in genomics.
Since the first human genome was sequenced in 2003, the cost of whole genome sequencing has steadily shrunk, far outstripping the pace of Moore’s law. That’s led to an explosion of genomic data, with the total amount of sequence data is doubling every seven months.
“The ability to sequence the human genome in its totality is incredibly powerful,” Huang said.
To put this data to work — and unlock the promise of truly personalized medicine — Huang announced that NVIDIA is working with Beijing Genomics Institute.
BGI is using NVIDIA V100 GPUs and software from Parabricks, an Ann Arbor, Michigan- based startup acquired by NVIDIA earlier this month — to build the highest throughput genome sequencer yet, potentially driving down the cost of genomics-based personalized medicine.
“It took 15 years to sequence the human genome for the first time,” Huang said. “It is now possible to sequence 16 whole genomes per day.”
Huang also announced the availability of the NVIDIA Parabricks Genomic Analysis Toolkit, and its availability on NGC, NVIDIA’s hub for GPU-optimized software for deep learning, machine learning, and high-performance computing.
Accelerated Robotics with NVIDIA Isaac
As the talk wound to a close, Huang announced a new version of NVIDIA’s Isaac software development kit. The Isaac SDK achieves an important milestone in establishing a unified robotic development platform — enabling AI, simulation and manipulation capabilities.
The showstopper: Leonardo, a robotic arm with exquisite articulation created by NVIDIA researchers in Seattle, that not only performed a sophisticated task — recognizing and rearranging four colored cubes — but responded almost tenderly to the actions of the people around it in real time. It purred out a deep squeak, seemingly out of a Steven Spielberg movie.
As the audience watched the robotic arm was able to gently pluck a yellow colored block from Hunag’s hand and set it down. It then went on to rearrange four colored blocks, gently stacking them with fine precision.
The feat was the result of sophisticated simulation and training, that allows the robot to learn in virtual worlds, before being put to work in the real world. “And this is how we’re going to create robots in the future,” Huang said.
Accelerating Everything
Huang finished his talk by by recapping NVIDIA’s sprawling accelerated computing story, one that spans ray tracing, cloud gaming, recommendation systems, real-time conversational AI, 5G, genomics analysis, autonomous vehicle and robotis, and more.
“I want to thank you for your collaboration to make accelerated computing amazing and thank you for coming to GTC,” Huang said.
The post As AI Universe Keeps Expanding, NVIDIA CEO Lays Out Plan to Accelerate All of It appeared first on The Official NVIDIA Blog.