Autonomous Vehicles for Social Good: Learning to Solve Congestion
We are in the midst of an unprecedented convergence of two rapidly growing
trends on our roadways: sharply increasing congestion and the deployment of
autonomous vehicles. Year after year, highways get slower and slower: famously,
China’s roadways were paralyzed by a two-week long traffic jam in 2010. At the
same time as congestion worsens, hundreds of thousands of semi-autonomous
vehicles (AVs), which are vehicles with automated distance and lane-keeping
capabilities, are being deployed on highways worldwide. The second trend offers
a perfect opportunity to alleviate the first. The current generation of AVs,
while very far from full autonomy, already hold a multitude of advantages over
human drivers that make them perfectly poised to tackle this congestion. Humans
are imperfect drivers: accelerating when we shouldn’t, braking aggressively,
and make short-sighted decisions, all of which creates and amplifies patterns
of congestion.
On the other hand, AVs are free of these constraints: they have low reaction
times, can potentially coordinate over long distances, and most importantly,
companies can simply modify their braking and acceleration patterns in ways
that are congestion reducing. Even though only a small percentage of vehicles
are currently semi-autonomous, existing
research
indicates that even a small penetration rate, 3-4%, is sufficient to begin
easing congestion. The essential question is: will we capture the potential
gains, or will AVs simply reproduce and further the growing gridlock?
Given the unique capabilities of AVs, we want to ensure that their driving
patterns are designed for maximum impact on roadways. The proper deployment of
AVs should minimize gridlock, decrease total energy consumption, and maximize
the capacity of our roadways. While there have been decades of research on
these questions, there isn’t an existing consensus on the optimal driving
strategies to employ, nor easy metrics by which a self-driving car company
could assess a driving strategy and then choose to implement it in their own
vehicles. We postulate that a partial reason for this gap is the absence of
benchmarks: standardized problems which we can use to compare progress across
research groups and methods. With properly designed benchmarks we can examine
an AV’s driving behavior and quickly assign it a score, ensuring that the best
AV designs are the ones to make it out onto the roadways. Furthermore,
benchmarks should facilitate research, by making it easy for researchers to
rapidly try out new techniques and algorithms and see how they do at resolving
congestion.
In an attempt to fill this gap, our CORL paper proposes 11 new benchmarks
in centralized mixed-autonomy traffic control: traffic control where a small
fraction of the vehicles and traffic lights are controlled by a single
computer. We’ve released these benchmarks as a part of Flow, a tool
we’ve developed for applying control and reinforcement learning (via using RLlib
and rllab as the reinforcement
learning libraries) to autonomous vehicles and traffic lights in the traffic
simulators SUMO and AIMSUN. A high score in these benchmarks
means an improvement in real-world congestion metrics such as average speed,
total system delay, and roadway throughput. By making progress on these
benchmarks, we hope to answer fundamental questions about AV usage and provide
a roadmap for deploying congestion improving AVs in the real world.
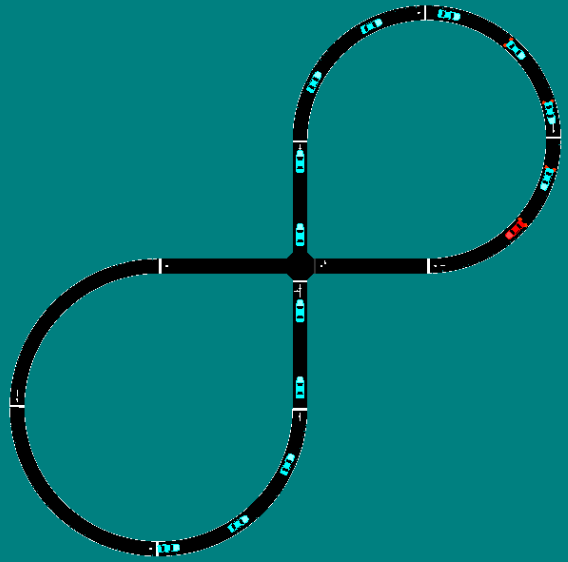
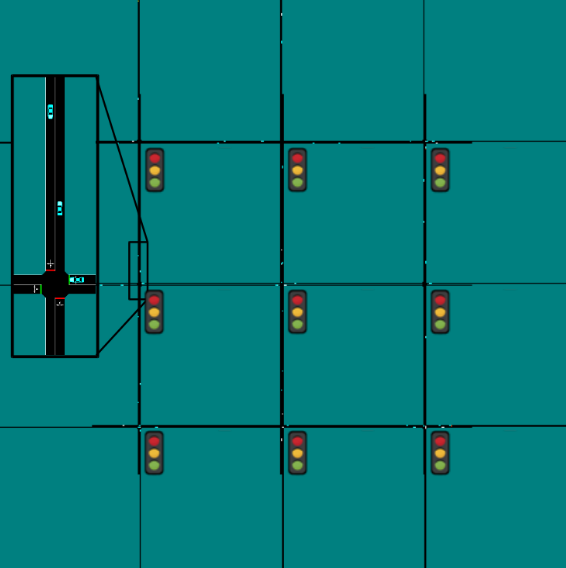
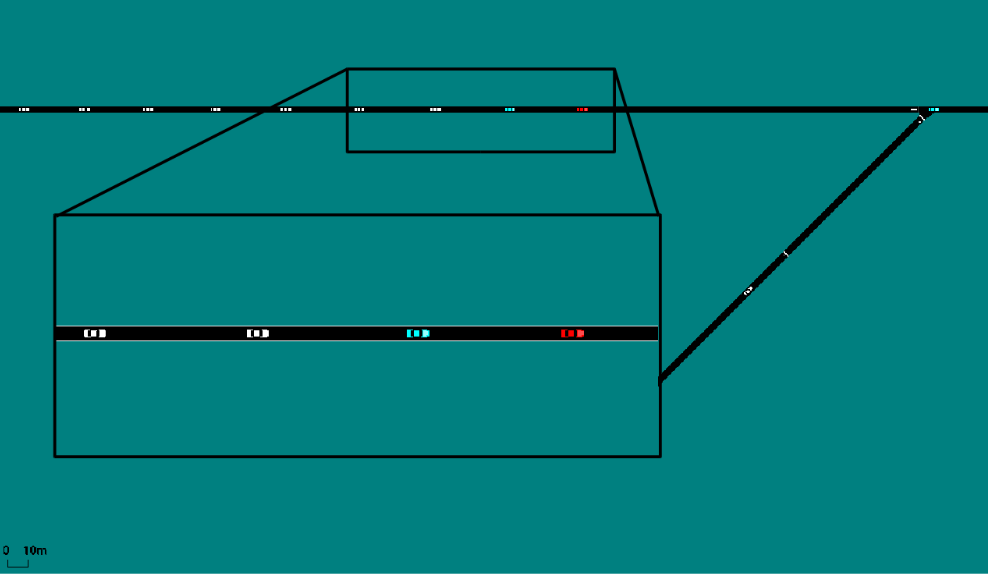
The benchmark scenarios, depicted at the top of this post, cover the following
settings:
-
A simple figure eight, representing a toy intersection, in which the optimal
solution is either a snaking behavior or learning to alternate which
direction is moving without conflict. -
A resizable grid of traffic lights where the goal is to optimize the light
patterns to minimize the average travel time. -
An on-ramp merge in which a vehicle aggressive merging onto the main highway
causes a shockwave that lowers the average speed of the system. -
A toy model of the San-Francisco to Oakland Bay Bridge where four lanes merge
to two and then to one. The goal is to prevent congestion from forming so to
maximize the number of exiting vehicles.
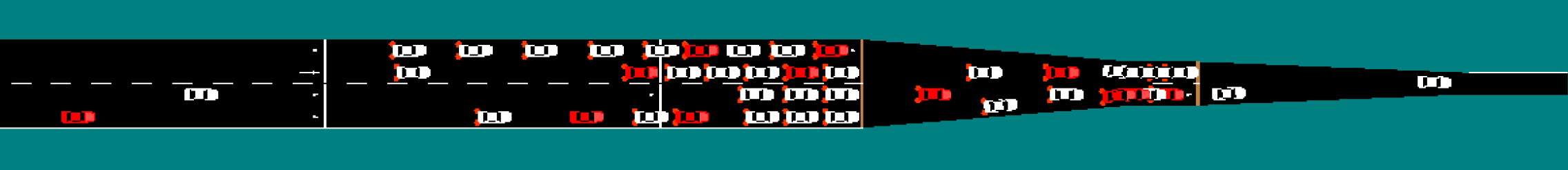
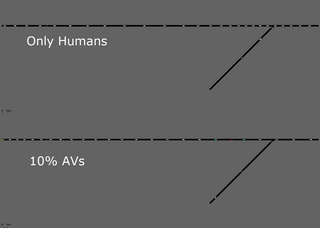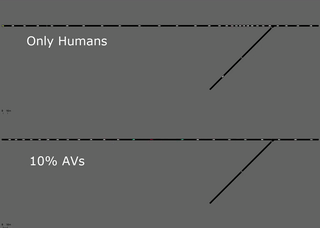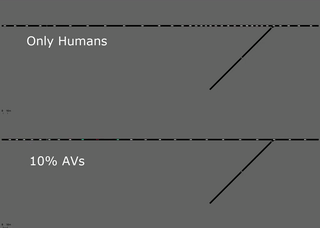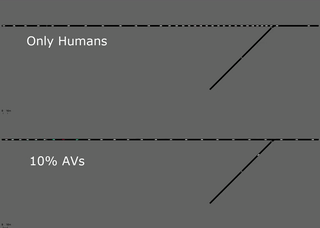
As an example of an exciting and helpful emergent behavior that was discovered
in these benchmarks, the following GIF shows a segment of the bottleneck
scenario in which the four lanes merge down to two, with a two-to-one
bottleneck further downstream that is not shown. In the top, we have the fully
human case in orange. The human drivers enter the four-to-two bottleneck at an
unrestricted rate, which leads to congestion at the two-to-one bottleneck and
subsequent congestion that slows down the whole system. In the bottom video,
there is a mix of human drivers (orange) and autonomous vehicles (red). We find
that the autonomous vehicles learn to control the rate at which vehicles are
entering the two-to-one bottleneck and they accelerate to help the vehicles
behind them merge smoothly. Despite only one in ten vehicles being autonomous,
the system is able to remain uncongested and there is a 35% improvement in the
throughput of the system.

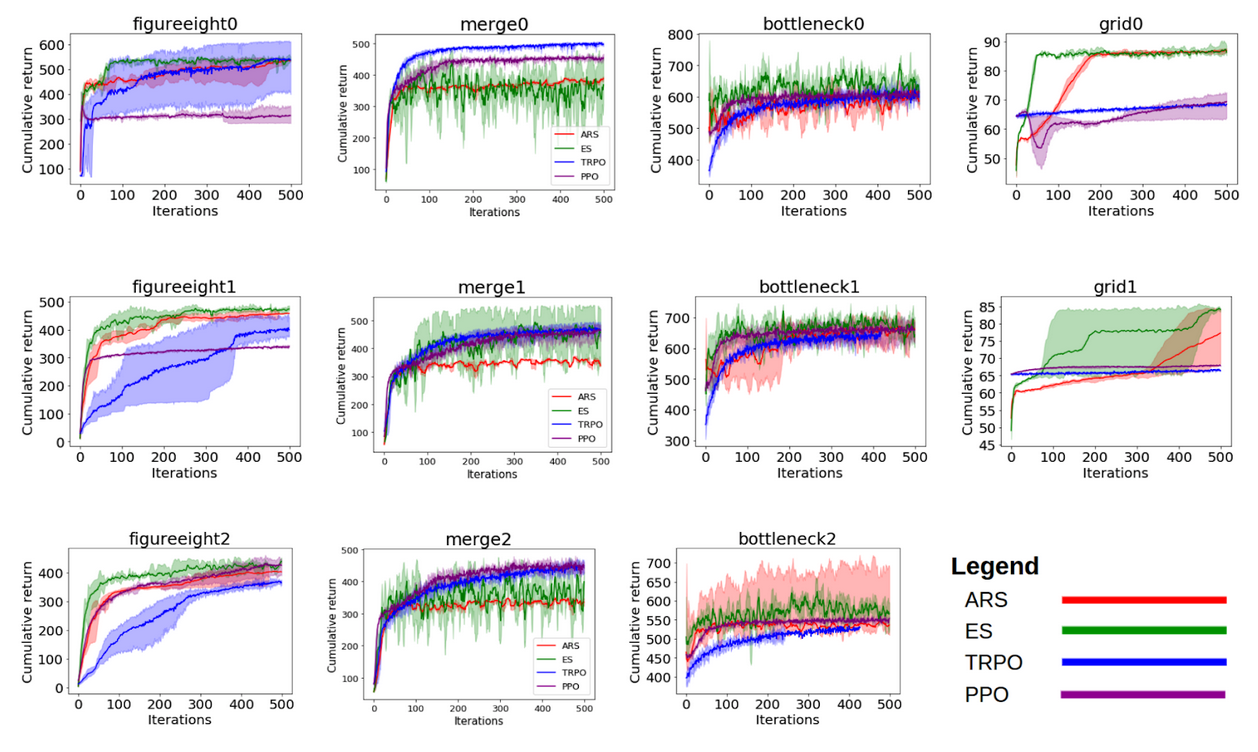
Once we formulated and coded up the benchmarks, we wanted to make sure that
researchers had a baseline set of values to check their algorithms against. We
performed a small hyperparameter sweep and then ran the best hyperparameters
for the following RL algorithms: Augmented Random Search, Proximal Policy
Optimization, Evolution Strategies, and Trust Region Policy Optimization. The
top graphs indicate baseline scores against a set of proxy rewards that are
used during training time. Each graph corresponds to a scenario and the scores
the algorithms achieved as a function of training time. These should make
working with the benchmarks easier as you’ll know immediately if you’re on the
right track based on whether your score is above or below these values.
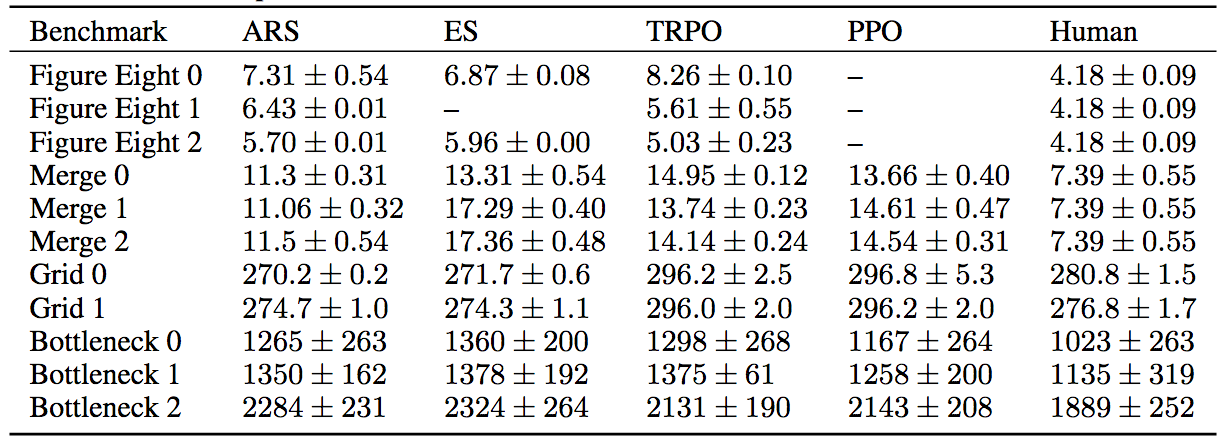
From an impact on congestion perspective however, the graph that really matters
is the one at the bottom, where we score the algorithms according to the
metrics that genuinely affect congestion. These metrics are: average speed for
the Figure Eight and Merge, average delay per vehicle for the Grid, and total
outflow in vehicles per hour for the bottleneck. The first four columns are the
algorithms graded according to these metrics and in the last column we list the
results of a fully human baseline. Note that all of these benchmarks are at
relatively low AV penetration rates, ranging from 7% at the lowest to 25% at
the highest (i.e. ranging from 1 AV in every 14 vehicles to 1 AV in every 4).
The congestion metrics in the fully human column are all sharply worse,
suggesting that even at very low penetration rates, AVs can have an incredible
impact on congestion.
So how do the AVs actually work to ease congestion? As an example of one
possible mechanism, the video below compares an on-ramp merge for a fully human
case (top) and the case where one in every ten drivers is autonomous (red) and
nine in ten are human (white). In both cases, a human driver is attempting to
aggressively merge onto the ramp with little concern for the vehicles on the
main road. In the fully human case, the vehicles are packed closely together,
and when a human driver sharply merges on, the cars behind need to brake
quickly, leading to “bunching”. However, in the case with AVs, the autonomous
vehicle accelerates with the intent of opening up larger gaps between the
vehicles as they approach the on-ramp. The larger spaces create a buffer zone,
so that when the on-ramp vehicle merges, the vehicles on the main portion of
the highway can brake more gently.
There is still a lot of work to be done; while we’re unable to prove it
mathematically, we’re fairly certain that none of our results achieve the
optimal top scores and the full paper provides some arguments suggesting that
we’ve just found local minima.
There’s a large set of totally untackled questions as well. For one, these
benchmarks are for the fully centralized case, when all the cars are controlled
by one central computer. Any real road driving policy would likely have to be
decentralized: can we decentralize the system without decreasing performance?
There are also notions of fairness that aren’t discussed. As the video below
shows, bottleneck outflow can be significantly improved by fully blocking a
lane; while this driving pattern is efficient, it severely penalizes some
drivers while rewarding others, invariably leading to road rage. Finally, there
is the fascinating question of generalization. It seems difficult to deploy a
separate driving behavior for every unique driving scenario; is it possible to
find one single controller that works across different types of transportation
networks? We aim to address all of these questions in a future set of
benchmarks.

If you’re interested in contributing to these new benchmarks, trying to beat
our old benchmarks, or working towards improving the mixed-autonomy future, get
in touch via our GitHub page or our
website!
Thanks to Jonathan Liu, Prastuti Singh, Yashar Farid, and Richard Liaw for
edits and discussions. Thanks to Aboudy Kriedieh for helping prepare some of
the videos.